Home
>
Archive
>
SSW Standards
>
Developer Access
>
SSW How to Improve Access Performance
How to Improve Access Performance
Compact your database often to reclaim space
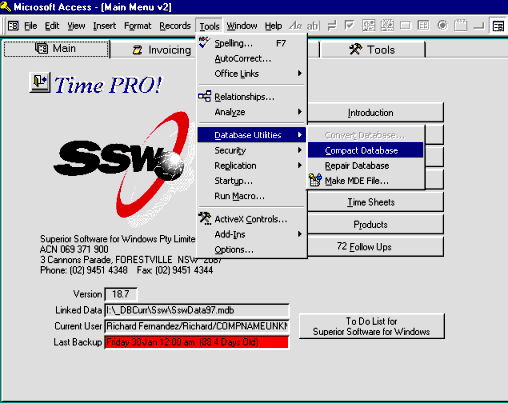
Compacting your database reclaims unused space and makes almost all
operations faster. You will do this on a regular basis. When you
compact the database, you reorganize records so that they are stored
in adjacent spaces, making retrieval faster. Additionally, compacting
a database updates its data statistics, which can be used by a query
to run faster. Defragmenting first is just academic.... You may want
to defragment your disk using a program such as the Disk Defragmenter
that ships with Windows 95 before compacting your database. This
leaves contiguous free disk space immediately after the database file.
In theory, this make future additions to the database occur faster.
-
You can force a query to recompile (which in turn causes it to use
the latest statistics) by opening it in design view, saving it, and
then running it.
-
Also be sure to compact anytime you import or delete objects in your
database, or compile and save VBA code.
Increase RAM
Increase the amount of RAM on your computer. The minimum acceptable
amount of RAM for Access 97 is 16 MB. 32 MB is better but 64 MB is
SSW's recommendation. Windows NT requires more RAM than Windows 95 to
achieve the same level of performance, so if you have the choice
always get 64 MB of RAM.
Keep Enough Local Hard Disk Space Free
Access requires a fair amount of disk space to operate, especially
with large databases. Operations such as running large action queries,
adding lots of data, importing data, and compiling and saving module
code can use a lot of additional space on a temporary basis.
Additionally, transactions and compacting the database can use a lot
of disk space. A good rule of thumb is to have roughly 5-10 times the
size of your largest database available in free local storage. SSW
recommends that you should always have at least 100 MB free.
Run on a Computer with a Pentium processor
Access requires a Pentium processor for adequate performance. A
DX4/100 MHZ processor is the minimum but a Pentium200 MMX is
recommended as the base Intel Processor.
Avoid Wallpaper
Avoid wallpaper, unless you are using a small, tiled bitmap.
Close Access Occasionally to Reclaim Leaked Memory
Almost all Windows applications "leak" memory. This is due to data
structures, variables and other memory consumers that are not
correctly released by applications. By closing Access, you allow
Windows to reclaim this leaked memory.
Close Unneeded Applications
Free up memory by closing applications that you aren't using. If you
are using the System Agent from the Microsoft Windows Plus Pack,
consider turning it off to make more memory available for your Access
application.
Disable Office Startup Programs
Office installs one or more startup programs in your
Windows\Start\Menu\Programs\Startup folder. Typically, the two
programs installed are the Office Fast Start and Office Find Fast
indexing utilities. Consider removing these items from the Startup
folder, as they use up memory. Additionally, the Find Fast indexer
runs continuously, and can dramatically reduce Access application
performance.
Don't Use Disk Compression Software
Do not use disk compression software on the drive where you have
installed Microsoft Access, or where your database file(s) are
located. Disk compression exacts a heavy toll on performance, and this
toll can be acute in database applications.
Don't Use RAM Disks
Don't waste RAM by using a RAM disk. RAM disks are a vestige of 16-bit
Windows and DOS systems, and have no place on modern computers.
Install Access Locally
Do not install Microsoft Access, or its related Microsoft Office
components on a network drive. Most applications, including Access and
Office perform better when run from local drives.
Install Windows Locally
The Windows operating system should be installed on a local fixed
drive on your computer. Because of the number of components involved
in running Windows, a network installation of Windows causes poor
performance, especially for database applications.
Keep Databases Local
Whenever possible, keep your databases local instead of on a network
drive. In almost all cases, local disk access is faster than network
access.
Adjust Virtual Memory Settings
Although Windows 95's default virtual memory settings are adequate for
most systems, you may want to consider lowering the settings if you
don't have a lot of space on the disk being used for virtual memory,
or you may wish to use another local drive that is faster than the one
being used by default for virtual memory.
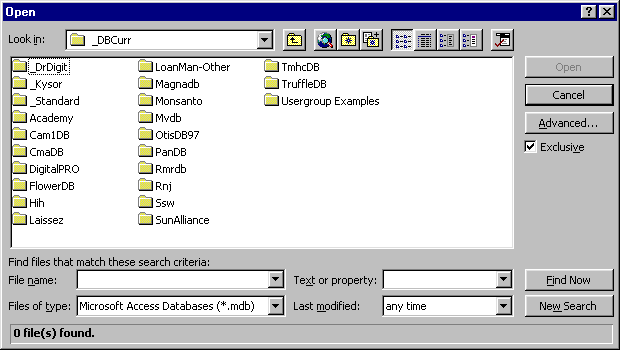
Open Databases Exclusively
If you are opening a database, and no other users need to use the
database, open the database in exclusive mode. To do this, check the
Exclusive checkbox in the Open Database dialog, as shown below.
Optimise your Disk
Keep your hard disk in optimal shape by deleting unneeded files and
emptying your Recycle Bin. Use a disk defragmenter, such as the one
found the Windows 95 Accessories, Systems tools menu.
Developers Only: Saving space with
single precision number fields
One of the most prevalent design problems we see with databases is the
unnecessary use of the Double number field. In some cases changing all
the double precision number fields in a table from double to single
real can trim the space used by about 40%. This makes a lot of
difference to performance in reading the file. You can store numbers
from -3.402823E38 to -1.401298E-45. Basically if the number is going
to have over 6 significant figures in it, then think very carefully
about this change as those precise number will get trimmed. An export
of the table to a text file will allow you recover if you do trim a
number incorrectly. Numbers such as 25.773 and -43000.1 dont need
double precision. Don't forget to compact your database after this
event.
Hint Courtesy of Garry Robinson.